Sholan R. et al., 2025: Long-Term Prospective Evaluation of Li-ESWT with or without PDE5 Inhibitors for Erectile Dysfunction following Nerve-Sparing Radical Prostatectomy.
Rashad Sholan 1 2, Rufat Aliyev 1, Seymur Karimov 3, Malahat Sultan 4, Anar Almazkhanli 3
1Scientific Research Center, State Security Service Military Hospital, Baku, Azerbaijan.
2Scientific Research Center, Azerbaijan Medical University, Baku, Azerbaijan.
3Department of Kidney Diseases and Organ Transplantation, State Security Service Military Hospital, Baku, Azerbaijan.
4Department of Radiology, Azerbaijan Medical University, Baku, Azerbaijan.
Abstract
Introduction: Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common complication following radical prostatectomy (RP). Although phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5is) are used for penile rehabilitation, their efficacy post-RP is limited. Low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy (Li-ESWT) has emerged as a potential noninvasive treatment, promoting tissue regeneration. This study evaluates the effectiveness of Li-ESWT, with or without PDE5i, for post-RP ED.
Methods: This prospective study included 104 patients who underwent nerve-sparing RP and received Li-ESWT. Patients were divided into two groups: group 1 received daily 5 mg tadalafil along with Li-ESWT, while group 2 received Li-ESWT alone. Erectile function was assessed using the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) at baseline, 6, 12, and 24 months postoperatively.
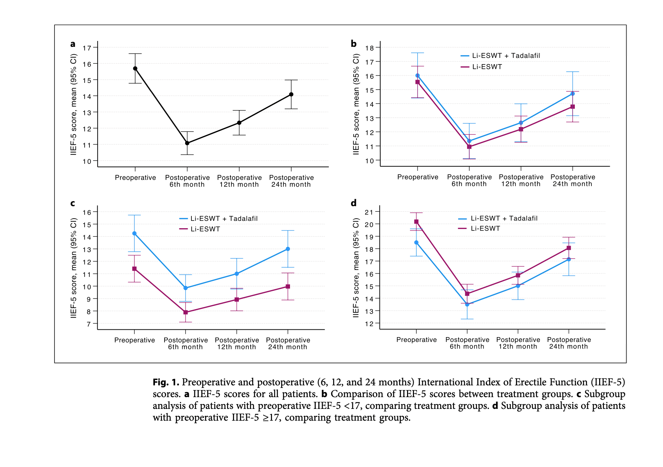
Results: The preoperative mean IIEF-5 score was 15.7 ± 4.7, with 54.8% of patients scoring below 17. Postoperatively, significant improvements in IIEF-5 scores were observed at 12 and 24 months in both groups compared to the 6th month. In patients with preoperative IIEF-5 <17, group 1 showed significantly greater improvement in IIEF-5 scores compared to group 2 (p = 0.008). No significant difference was observed between the groups in patients with preoperative IIEF-5 ≥17 (p = 0.893).
Conclusion: Li-ESWT is an effective treatment for ED following nerve-sparing RP, with or without PDE5i. In patients with mild-to-moderate or greater preoperative ED, the combination of PDE5i and Li-ESWT may provide additional benefits, whereas Li-ESWT alone appears sufficient for those with milder cases.
Urol Int. 2025 May 11:1-7. doi: 10.1159/000546359. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40349678


Comments 1
Introduction: Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common complication after radical prostatectomy (RP) for localized prostate cancer, affecting a significant percentage of men, despite the nerve-sparing techniques used. Current treatments include phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5is), but their effectiveness is often limited. Low-intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapy (Li-ESWT) is emerging as a noninvasive treatment option that may improve ED recovery through promoting tissue regeneration and vascularization.
Study Design: This prospective study evaluated the efficacy of Li-ESWT for ED following nerve-sparing RP in Azerbaijan, involving patients who underwent surgery between October 2017 and November 2023. Patients were divided into two groups: one receiving daily tadalafil (a PDE5i) with Li-ESWT, and the other receiving Li-ESWT alone.
In the group receiving PDE5i, daily 5 mg tadalafil was initiated in the third postoperative week. Li-ESWT (DUOLITH® SD1 T-TOP, Storz Medical AG, Tägerwilen, Switzerland) was started 2 months postoperatively, with a total of 12 sessions performed twice weekly. A total of 3,000 shockwaves were applied at an energy density of 0.25 mJ/ mm2 and an emission frequency of 6 Hz,
Key exclusion criteria included previous penile procedures and severe comorbidities. The IIEF-5 score was used to assess erectile function at multiple time points postoperatively.
Results: A total of 104 patients were included.Baseline characteristics were similar across groups.
- The IIEF-5 scores significantly dropped postoperatively at the 6-month mark before showing improvement at 12 and 24 months.
- Although improvements were seen in both groups, there was no statistically significant difference in IIEF-5 score changes between the group receiving PDE5i and Li-ESWT and the group that received Li-ESWT alone.
- In patients with preoperative IIEF-5 scores less 17, Li-ESWT combined with PDE5i showed greater improvements compared to Li-ESWT alone.
Thus, the efficacy of the combined treatment depends on the prepoperative status of erectile function.
Discussion: Li-ESWT demonstrated effectiveness in improving erectile function post-RP, particularly among patients with more severe preoperative ED. The study highlights the potential of Li-ESWT as part of a penile rehabilitation strategy, especially in settings where advanced surgical options like robotic-assisted surgeries are unavailable.
Limitations: The study’s limitations include a relatively small sample size (N=104) and most importantly the lack of randomization, which may bias the results. Larger studies with more diverse cohorts are needed to further validate these findings.
Conclusions: Li-ESWT, with or without PDE5 inhibitors, appears to be a beneficial treatment for ED following nerve-sparing RP, particularly for patients with mild to moderate preoperative erectile issues. Continued exploration of long-term outcomes and larger trials will help establish its efficacy in this context.
Jens Rassweiler